EIT RawMaterials Projects
The ambitious vision of EIT RawMaterials is realised by the creation of a structured collaboration within the Knowledge Triangle, which is the basis of the EIT model.
Call for Innovation & Education Projects is now open!
EIT RawMaterials Projects Timeline
InnoLOG: Innovative geophysical logging tools for mineral exploration
InnoLOG: Innovative geophysical logging tools for mineral exploration

Project duration: 1 April 2017 – 31 March 2020
Objective
This project will impact by boosting of the competitiveness, of the European raw materials companies and providing innovative solutions for a more efficient and sustainable exploration. This proposal contributes with innovative advances in a range of technologies with high impact in the value chain, together with developments in technologies and innovative solutions. The main objective of the project is to improve the performance of the existing downhole geophysical logging tools in the identification of specific minerals in the subsurface and mineral deposits evaluation. Innovative borehole logging tools based on recently developed sensors and innovative processing capabilities provide new opportunities for development of efficient downhole exploration tools suitable for detection and quantification of minerals and raw materials in the subsurface. Extensive testing of the tools’ performance first at research facilities and in mines is planned to demonstrate the efficiency of the new geophysical logging tools as high cost-effectiveness raw materials exploration tools and mineral diagnostic performance.
The solution (technology)
InnoLOG will focus on innovation activities on:
- Applying innovations on borehole geophysical logging to mining activities.
- Implementing new sensors in innovative borehole logging tools.
- Testing and validation in different types of mines.
- Design and preliminary testing of future logging tools.
- Training in the use of the innovative technologies.
Partnership
- Agencia Estatal Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cientificas, CSIC (Spanish National Research Council), Spain (Lead Partner)
- Consell general de Cambres de Comerc Industria i Navegacio de Catalunya (General Council of the Catalan Chambers of Commerce), Spain
- Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (CNR), Italy
- Geological Survey of Slovenia, GeoZS, Slovenia
- Geological Survey of Sweden, SGU, Sweden
- Magnesitas Navarras S.A., Spain
- Universidad Politecnica de Catalunya (UPC Sarti), Spain
- Universidad Politecnica de Madrid, UPM (Technical University of Madrid), Spain
For more information, please visit the project website.
INNOMAT: Innovation Management through integration of LCA Training Packages
INNOMAT: Innovation Management through integration of LCA Training Packages
Project duration: 01 January 2018 – 31 December 2019
Objective
EIT RawMaterials offers companies solutions to their risks with Critical Raw Materials (CRMs) in their products, however, many companies are not aware of any risks. They are interested in Life Cycle Assessments (LCAs), but these are laborious or expensive. Innomat offers with a course for companies an affordable insight in LCA’s and CRM-risks, and methods on how to be more resource resilient. Many methods are from the KIC-RM community, which makes this KAVA a contribution to build-up the KIC-RM community. See full details on the INNOMAT course.
The solution (technology)
Performing an LCA for products or processes gives a company valuable information on its environmental footprint. An LCA could also help to map the risks of Critical Raw Materials (CRMs) for the company’s operation. However, the existing LCA-method is complex, laborious, not focussed on business solutions, not integrated in operational excellence management tools aiming at innovation, and does not give any overview of risks CRM’s can have for operations. This KAVA offers two sets of training material:
- Innovative LCA/CRM teaching material that makes LCA benchmarking and CRM analyses more accessible to SMEs, and easier to use. There will be a focus on recycling and renewable resources, and attention will be drawn to the risk of CRMs in products.
- Teaching material for Product & Business Innovation (i.e. eco-efficient value creation of innovative products and services, and how to apply the results of LCA/CRM in the circular economy).
The course is aimed at designers, engineers and business managers.
Partnership
- Technische Universiteit Delft (Delft University of Technology), Netherlands (Lead Partner)
- Ghent University, Belgium
- Institut polytechnique de Grenoble (INP Grenoble Institute of Technology), France
- Wuppertal Institut für Klima, Umwelt, Energie GmbH (Wuppertal Institute), Germany
- Zavod za gradbenistvo Slovenije (ZAG Slovenian National Building and Civil Engineering Institute), Slovenia
For more information, please visit the project web page.
Innovation-Incubator: Potential for Local Ecosystem Inno-Centres in ESEE Region
Innovation-Incubator: Potential for Local Ecosystem Inno-Centres in ESEE Region
Project duration: 1 January 2020 – 31 December 2021
Objective
The project aims at enhancing the innovation capacity within the ESEE region by establishing individual concepts for regional ecosystem effective university-based incubators based on joint knowledge transfer and individual concept development. This will happen aligned with the ECLC Business Creation & Support activities and programs in the ESEE region and will be verified with actual start-ups. Minimum 6 RIS task partners (2 Universities, minimum 4 start-ups) will join the initial consortium. The project will show a one-year concept phase, followed by a one-year implementation period – but shall become sustainable on long term.
The solution (technology)
Even though university-based incubators have become a common part of innovation systems, they often do not manage to assume their role of innovation boosters in the national and regional ecosystems. This is especially because they fail at creating strong links to the key players in the regional innovation ecosystems, such as research institutions, industry, public sector and existing entrepreneurship initiatives – but also aligned with EIT KIC activities. Furthermore, they often lack a systematic approach to innovation as well as knowledge on innovation schemes.
As response to these problems, the outlined project aims in general at jointly developing specific tailor-made concepts for regional university-based incubators in the raw materials and related sectors in East and South-East Europe, focussing on the local/regional ecosystems and using the knowledge and experience of the project participants for enhancing their innovation capacity. Moreover, the KIC good practices of the Knowledge Triangle Integration (academia – business – qualification) will be transferred from the concept phase on, making the ecosystems integral parts of the innovation incubators and strengthening the role of the universities in their regional innovation ecosystems (create knowledge and job opportunities for graduates, attract industry, etc.). Incubators will be able to engineer and deliver added-value services to the regional entrepreneurial community and thus, foster the creation of innovative and sustainable start-up companies with a focus on raw materials and related sectors or cross-sectional technologies.
As the ECLC of EIT RM has the overall scope to develop and support related ecosystems in the ESEE region it already reaches out to local incubators and ecosystems in the region with the aim to identify relevant idea holders and (potential) start-up in these countries, to ultimately increase the participation from these countries in the KIC´s Business Creations & Support programs and thus, create impact on those ecosystems.
The Innovation-Incubator project activities (and especially beyond the project phase) shall be aligned with these outreach activities of the ECLC, meaning that – by transferring the knowledge and good practice from more established ones into those that need capacity building – one significant objective of the project is to contribute to the ECLC´s “BC&S Plan for RIS Countries”, helping to create start-ups from the KIC´s Education and Innovation projects. In fact the Incubators involved in this project shall be enabled and supported to contribute to these KIC´s objectives, measurable by countable results. Therefore, already in the project phase itself, the theoretical approach of the project shall be verified by bringing along, supporting or even creating start-ups by each of the participating University Incubators and integrating them into the project.
Partnership
- Slovak University of Technology in Bratislava (STU), Slovakia
- Tallinn University of Technology, Estonia
- Technical University of Kosice, Slovakia
- University of Miskolc, Hungary
- Zentrum für angewandte Technologie Leoben GmbH, Austria
- Montanuniversität Leoben (Lead Partner), Austria
InPhos: Sustainable Management of Phosphorus in Baltic countries
InPhos: Sustainable Management of Phosphorus in Baltic countries
Project duration: 1. January 2018 – 31 March 2020
Objective
Phosphorus is a critical raw material and its sustainable management needs to be implemented in all European regions. It is an essential element for human nutrition, yet limited resource, which cannot be replaced by any other element. As Europe has no significant phosphorous mines, it is highly dependent on the import of phosphorous ore. In the last years, European countries have already taken actions in order to achieve security in phosphorous supply on the continent. In Switzerland and Germany, a regulatory framework relating to the recovery of phosphorus has been introduced. It can be expected that in other countries, such a regulatory framework will be introduced in the near future. Due to the fact that in Baltic supply chains, the current usage of phosphorous involves waste and losses at every stage of its lifecycle, and one of the most interesting areas which has significant problems associated with improper management of phosphorous is the Baltic region.
The solution (technology)
In InPhos, a working group of experts from developed countries and the Baltic region will jointly develop a strategy for the Baltic countries, via the transfer of knowledge and design of modern solutions for a sustainable use of phosphorous. InPhos will also raise awareness among stakeholders on the implications of the scarcity of this raw material in Europe
Partnership
- Mineral and Energy Economy Research Institute of the Polish Academy of Sciences (MEERI), Poland (Lead Partner)
- Alma Mater Studiorum – Universita di Bologna, Italy
- BIONOR Sp. Z.o.o, Poland
- Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung (BAM), Germany
- Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden
- Geological Survey of Finland (GTK), Finland
- Kauno Technologijos Universitetas (Kaunas University of Technology), Lithuania
- Kauno vandenys Ltd., Lithuania
- Outotec Deutschland GmbH, Germany
- Riga Technical University, Latvia
- Tallinn University of Technology, Estonia
- University of Latvia, Latvia
For more information, please visit the official website of the project.
INSite: Insitu ore grading system using LIBS in harsh environments
INSite: Insitu ore grading system using LIBS in harsh environments
Project duration: 1 January 2020 – 31 December 2022
Objective
LIBS (Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy) is a promising tool for realtime analysis of low atomic weight critical raw materials such as Li. Solution on the market are plagued by inconsistent results and poor quantification performance. INsite introduces a new solution where the concept of information transfer coupled with advanced AI algorithms and a knowledge database of mineral spectra enables true in-situ ore grading with a new generation of smart LIBS technology.
The solution (technology)
INSite brings together a multidisciplinary research team with a renowned spectroscopy company to take to the market a new smart LIBS (Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy) technology. LIBS is a powerful spectroscopy technique for element analysis with very promising features for real time assessment of composition. However, in spite of many systems already probing the market, its performance is only acceptable with simple samples and in controlled conditions. Its identification and quantification abilities rapidly decline with sample complexity and environmental roughness (e.g. underwater). To date no satisfactory system presents acceptable performance when facing complex mineral samples in harsh mining conditions.
Recently, however, our team has developed novel methods that allow LIBS technology to perform with accurate analytical performance even with complex mineral samples, thus enabling real time ore grading. This was achieved under the framework of Horizon 2020 VAMOS project [http://vamos-project.eu/], where the technology was validated in a relevant mining environment (TRL6). The technology is in a mature state and is ready to be improved to the market under the efforts of INSite project. INSite aims to bring to market a unique and integrated LIBS technology suitable to perform accurately in harsh mining environments with true analytical capabilities. The Smart-LIBS technology involves an improved concept which is based on novel Artificial Intelligence algorithms with advanced self-learning strategies, coupled with an extensive knowledge-database of spectra and analytical information of complex minerals. Comparative lab tests with other systems in the market have shown, in a test case of lithium minerals a superior performance, with good accuracy and free of the false negative and false positive indications which plagued the commercial systems.
Using patented calibration transfer methods, the technology can be incorporated in different hardware configurations enabling a new set of tools for smart mining, suitable for both exploration and exploitation stages. The project will deliver a new portable smart LIBS system suitable for insitu identification and quantification of minerals, particularly suited for low atomic number elements, such as Lithium, where the regular technologies such as XRF do not work. In addition, exploratory works will prepare next generation of the product to work underwater, unveiling the new market of the mining activity.
The equipment has huge potential to improve the efficiency and reduce the costs and environmental foot print of mining operations. Furthermore, having such analytical capabilities in situ, is also an asset in many other fields of application and potential markets: geosciences research/services, oil and gas research and development fields.
Partnership
- National Research Council, Italy
- Geological Survey of Slovenia (GeoZS), Slovenia
- Ghent University, Belgium
- LSA – Laser Analytical Systems & Automation GmbH, Germany
- LTB Lasertechnik Berlin GmbH, Germany
- Metrohm AG, Switzerland
- Rheinisch-Westfaelische Technische Hochschule Aachen (RWTH Aachen), Germany
- Technische Universiteit Delft (Delft University of Technology), Germany
- Institute for Systems and Computer Engineering, Technology and Science (Lead Partner), Portugal
inSPECtor: Integrated spectroscopy sensor system for laser-induced fluorescence and hyperspectral imaging
inSPECtor: Integrated spectroscopy sensor system for laser-induced fluorescence and hyperspectral imaging
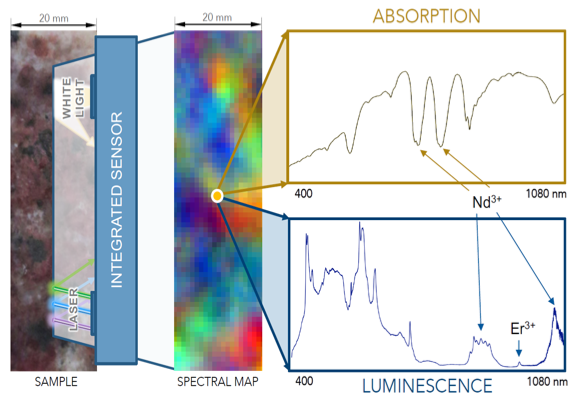
Project duration: 1 April 2017 – 31 March 2020
Objective
Contribution to the overall impact of the inSPECTor project is a push forward in entrepreneurship by bringing together the most important technological key players and leaders. With the aim of placing a breakthrough product on the raw materials market and so ultimately addressing the key issues in increased resource and energy efficiency thanks to an effective reduction in environmental impacts (data acquisition involves no traditional chemical sample processing techniques) but also thanks to an increased response time (data acquisition for 1 m of drill core will take approximately 10s). inSPECTor is a joint research and development project and also involves an educational component to it. This relates to the supervision of a PhD student who will be based at HZDR-HIF and will be part of the research team on hyperspectral data processing and drill core imaging. She/he will closely collaborate with researchers at the TUBAF on luminescence spectroscopy and data processing routines. The PhD student will link the research components of inSPECTor with the technical implementation developed by the two SME task partners enabling effective and clear flow of information.
The solution (technology)
The integrated sensor system developed within the inSPECTor project is beneficial also for other partners in the EIT RawMaterials community, especially for those working in the theme on exploration and raw material resource assessment. The innovation in spectral sensors contributes to strengthening the competitiveness and capacities for further innovation due to the efficient solution for fast mineral mapping of drill cores with a high spatial resolution. Very important for the European raw material sector is also the ability of an efficient REE identification to reduce the import dependencies of those critical raw materials. Outside the consortium, the project inSPECTor contributes to the innovation capacity of the European raw material sector, because the developed sensor system could be also integrated into many future solutions and projects: Possible combination of emission and absorption spectroscopy with other sensor systems, an option that is not yet reflected in the current trend of modular multi-sensor systems. High potential is seen in combinations with other sensors for spectroscopy such as those for time-gated raman or x-ray fluorescence or with sensors that allow looking below the drill core surface such as tomography. Further developments may allow UAV-based exploration with the integrated spectral sensor system and can then complement multi-sensor solutions for UAV (e.g. multi-sensor drone up-scaling project lead by GEUS)- The time- and cost-efficient technology can support developments in online process control such as for exploitation monitoring or material sorting during material processing and recycling (quality control, process correction). The new analytical options have indirect benefits for further geoscientific fields (structural geology as supplementary info for exploration, genesis and differentiation of lithologic/geologic units, provenance analyses, REE as tracer/fingerprinting in material cycles).
Partnership
- Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf e.V. (HZDR), Germany (Lead Partner)
- Freiberg Instruments GmbH, Germany
- Geologian tutkimuskeskus, GTK (Geological Survey of Finland), Finland
- Specim, Spectral Imaging Ltd., Finland
- Technische Universität Bergakademie Freiberg (TUBAF), Germany
INSPIRE: Intensified Flow Separator Infrastructure and Expertise Network
INSPIRE: Intensified Flow Separator Infrastructure and Expertise Network
Project duration: 1 October 2016 – 30 September 2019
Objective
The INSPIRE network brings infrastructure & expertise together on innovative and breakthrough Process Intensification technologies for continuous separation of critical materials. These process intensification technologies strive to maximize the transfer of mass, momentum and heat and hence drastically increase separation efficiencies. The network aims at identifying the promising intensification technologies for the particular aim of separating and purifying metal ions, metal oxides and metal salts from liquid mixtures.
The solution (technology)
The infrastructure consists of structured flow systems, possibly actuated with non-contact energy forms such as light, ultrasound, microwaves, electrical fields, etc. These systems are used for intensifying separation processes in the fields of crystallization, precipitation, chromatographic separation, reactive extraction and membrane separation.
Partnership
- Katholieke Universiteit te Leuven (KU Leuven), Belgium (Lead Partner)
- Arkema, France
- Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (CNR, National Research Council), Italy
- Kungliga Tekniska Högskolan, KTH (Royal Institute of Technology), Sweden
- Lodz University of Technology, Poland
- MEAM BVBA, Belgium
- Technische Universiteit Delft (Delft University of Technology), the Netherlands
- University of Limerick, Ireland
For more information, please visit the project website.
INSPIREE project to build Europe’s first industrial-scale rare earth elements recycling plant
INSPIREE project to build Europe’s first industrial-scale rare earth elements recycling plant
Project Code: 70010_LIFE22-Env-IT-INSPIREE 101113882
General Introduction
The INSPIREE project, supported by EIT RawMaterials, is set to establish Europe’s first industrial-scale plant dedicated to recycling rare earth elements (REEs) from end-of-life permanent magnets (PMs). This innovative initiative focuses on recovering critical materials such as neodymium, praseodymium, and dysprosium from obsolete hard disk drives and electric motors. The INSPIREE project is a significant step towards reducing Europe’s dependency on imported REEs, which currently accounts for approximately 98% of its needs.
Objective
Europe’s demand for REEs is expected to increase fivefold by 2030, driven by the growth of renewable energy and electric mobility sectors. However, significant geological and processing barriers hinder domestic extraction. To address this, the INSPIREE project aims to bolster European self-reliance by recovering around 700 tons of REE oxalates annually by March 2027. This strategic venture seeks to secure a sustainable and steady supply of these critical raw materials.
Solution
The INSPIREE project, based in Ceccano, Italy, and funded by CINEA under the LIFE Program, is led by a consortium that includes EIT RawMaterials, Itelyum, GlobEco, Erion, and Università degli Studi dell’Aquila. Building on the successful New-RE pilot project, the INSPIREE initiative employs an innovative two-tiered process:
- Disassembly of Electric Rotors: Conducted at GlobEco’s facility, this first stage is designed to handle 1,000 tons of material annually.
- Extraction of REE Oxalates: The second stage involves hydrometallurgical processes at Itelyum’s plant, expected to process 2,000 tons of permanent magnets each year.
This approach offers significant technical advantages and environmental benefits, including improved chemical and water reuse.
EIT RawMaterials leverages its extensive network to enhance the project’s impact. By sharing results with partners, establishing new public and private partnerships, and engaging potential investors, EIT RawMaterials aims to ensure the INSPIREE project significantly contributes to creating a sustainable and secure supply of REEs for Europe.
Dates
- Project starting date: 1 October 2023
- Project end date: 31 March 2027
- Project duration: 42 months
Partners

INSPIRES: INtelligent and Sustainable Processing of Innovative Rare-Earth magnetS
INSPIRES: INtelligent and Sustainable Processing of Innovative Rare-Earth magnetS
Project duration: 1 January 2021 – 31 December 2023
Objective
There is a strong need to implement Rare-Earths recycling technologies in large-scale systems. The INSPIRES project aims at recovering and supplying Rare-Earths within the EU through radical innovations in the recycling of permanent magnets, focusing on one of the most readily available sources: home appliances. INSPIRES will optimize methods at industrial scale for sustainable extraction and recycling and use of recycled magnets in new motors.
The solution (technology)
The future of renewable energy and smart mobility depends upon permanent magnets (PMs), and those magnets depend upon Rare Earth Elements (REEs). From wind turbines and hydroelectric generators to electromotors in next-generation hybrid and electric vehicles, magnets are critical to Europe’s future. The essential Critical Raw Materials (CRM) used in NdFeB PMs are REEs, plus the non-REEs niobium and gallium. Except for niobium, overall recycling rates of these elements are close to zero; in Europe, there are no commercial installations for recycling of NdFeB PMs. Although CRMs from China have been the primary source for Europe, supplies are uncertain, and the Chinese production chain is generally unsustainable. At the same time, the demand for REEs for making new PMs is projected to double in 15 years. The INSPIRES (INtelligent and Sustainable Processing of Innovative Rare-Earth MagnetS) project seeks to address this challenge within a RIS Region (Slovenia) through radical innovations in the recycling of permanent magnets, focusing on the most common and readily available source of economically recyclable electric motors: home appliances such as washing machines, tumble driers, and similar devices. Unlike other sources of end of life (EOL) PMs, there are already well-functioning systems for the collection and dismantling of home appliances, but no procedures to enable recovery of magnets. We will develop new dismantling and recovery procedures for PMs on highly functional scrap and reproduction lines, pilot test new circular economy pathways with key industrial partners in their existing workflow contexts, analyze their sustainability performance from economic, environmental life cycle, and quality of life perspectives, and make recommendations for novel standardized marking of magnets and packing boxes. The project will aggregate results and innovations across the stakeholder space, including EU projects and clustering initiatives, and offer open and flexible new methods for easy adoption across Europe.
Partnership
- Centre for European Policy Studies (CEPS), Belgium
- National Research Council, Italy
- Domel, Elektromotorji in gospodinjski aparati, d.o.o, Slovenia
- Gorenje gospodinjski aparati, d.o.o., Slovenia
- Jozef Stefan Institute, Slovenia
- KOLEKTOR KFH, Pogonski sistemi in komponente d.o.o., Slovenia
- Pforzheim University of Applied Sciences, Germany
- Surovina družba za predelavo odpadkov d.o.o., Slovenia
- Technical University of Denmark, Denmark
- ZEOS, ravnanje z električno in elektronsko opremo, d.o.o., Slovenia
- Spanish National Research Council (Lead Partner), Spain






